Main code. More...
#include <Arduino.h>#include "config.h"#include "calibration.h"#include "processing.h"#include "types.h"#include "utils.h"#include "utils_relay.h"#include "utils_display.h"#include "utils_oled.h"#include "utils_temp.h"#include "validation.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| void | checkDiversionOnOff () |
| Checks and updates the diversion state. | |
| bool | forceFullPower () |
| Forces all loads to full power. | |
| void | handlePerSecondTasks (bool &bOffPeak, int16_t iTemperature_x100) |
| Handles tasks that need to be executed every second. | |
| void | loop () |
| Main processor loop. | |
| bool | proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverriding (const int16_t currentTemperature_x100) |
| Handles load priority rotation and overriding logic. | |
| bool | proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverridingDualTariff (const int16_t currentTemperature_x100) |
| Handles load priority in combination with dual tariff. | |
| void | proceedRotation () |
| Rotates the load priorities. | |
| void | processCalculationsForLogging () |
| Performs calculations on data for logging purposes. | |
| void | setup () |
| Called once during startup. | |
| void | updateTemperature () |
| Updates the temperature readings and sends a new request for the next cycle. | |
Detailed Description
Function Documentation
◆ checkDiversionOnOff()
| void checkDiversionOnOff | ( | ) |
Checks and updates the diversion state.
This function monitors the state of the diversion pin to determine whether the diversion is active or not. If the diversion pin state changes, it updates the b_diversionEnabled flag accordingly. Additionally, if debugging is enabled, it logs the state transitions (e.g., "Trigger diversion OFF!" or "End diversion OFF!") to the debug output.
- Note
- This function is only executed if the
DIVERSION_PIN_PRESENTcompile-time constant is defined.
- See also
- getPinState
- ENABLE_DEBUG
Definition at line 270 of file main.cpp.
References Shared::b_diversionEnabled, DBUG, DBUGLN, DIVERSION_PIN_PRESENT, diversionPin, and getPinState().
Referenced by handlePerSecondTasks().


◆ forceFullPower()
| bool forceFullPower | ( | ) |
Forces all loads to full power.
This function overrides the normal load control logic and forces all loads to operate at full power. It checks the state of the override pin and updates the override flags for all loads accordingly. If debugging is enabled, it logs the state transitions (e.g., "Trigger override!" or "End override!") to the debug output.
Key operations include:
- Checking the state of the override pin.
- Updating the override flags for all loads.
- Logging state transitions if debugging is enabled.
- Returns
- true if the override is active and all loads are forced to full power.
- false if the override is not active.
- Note
- This function is only executed if the
OVERRIDE_PIN_PRESENTcompile-time constant is defined.
- See also
- getPinState
- ENABLE_DEBUG
Definition at line 55 of file main.cpp.
References Shared::b_overrideLoadOn, DBUGLN, forcePin, getPinState(), and OVERRIDE_PIN_PRESENT.
Referenced by handlePerSecondTasks().


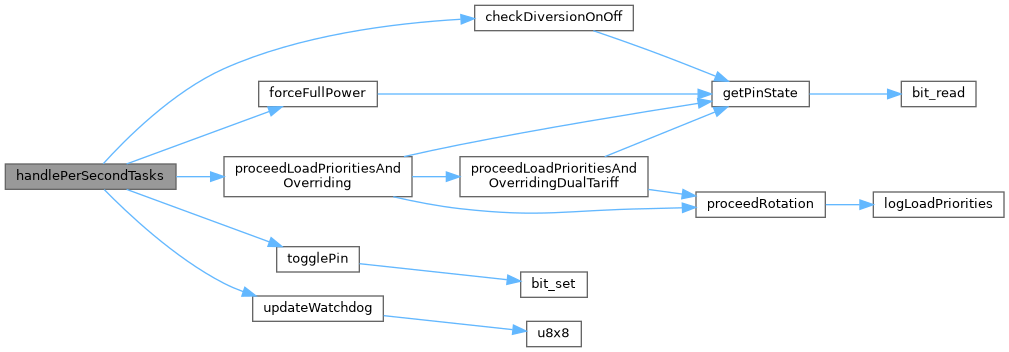
◆ handlePerSecondTasks()
| void handlePerSecondTasks | ( | bool & | bOffPeak, |
| int16_t | iTemperature_x100 ) |
Handles tasks that need to be executed every second.
This function performs a series of operations that are executed once per second. These include updating the absence of diverted energy count, toggling the watchdog pin (if present), updating the watchdog, checking the diversion state, managing load priorities and overrides, and refreshing the display. It also handles relay operations if relay diversion is enabled.
- Parameters
-
bOffPeak A reference to a boolean indicating whether the off-peak tariff is active. This value may be updated based on load priorities and overriding logic. iTemperature_x100 The current temperature multiplied by 100 (e.g., 25.00°C is represented as 2500). Used for temperature-based logic, such as load overrides.
- Note
- This function relies on several compile-time constants and global variables, such as
WATCHDOG_PIN_PRESENT,RELAY_DIVERSION, andEDD_isIdle.
Definition at line 441 of file main.cpp.
References checkDiversionOnOff(), forceFullPower(), proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverriding(), RELAY_DIVERSION, relays, togglePin(), updateWatchdog(), WATCHDOG_PIN_PRESENT, and watchDogPin.
Referenced by loop().

◆ loop()
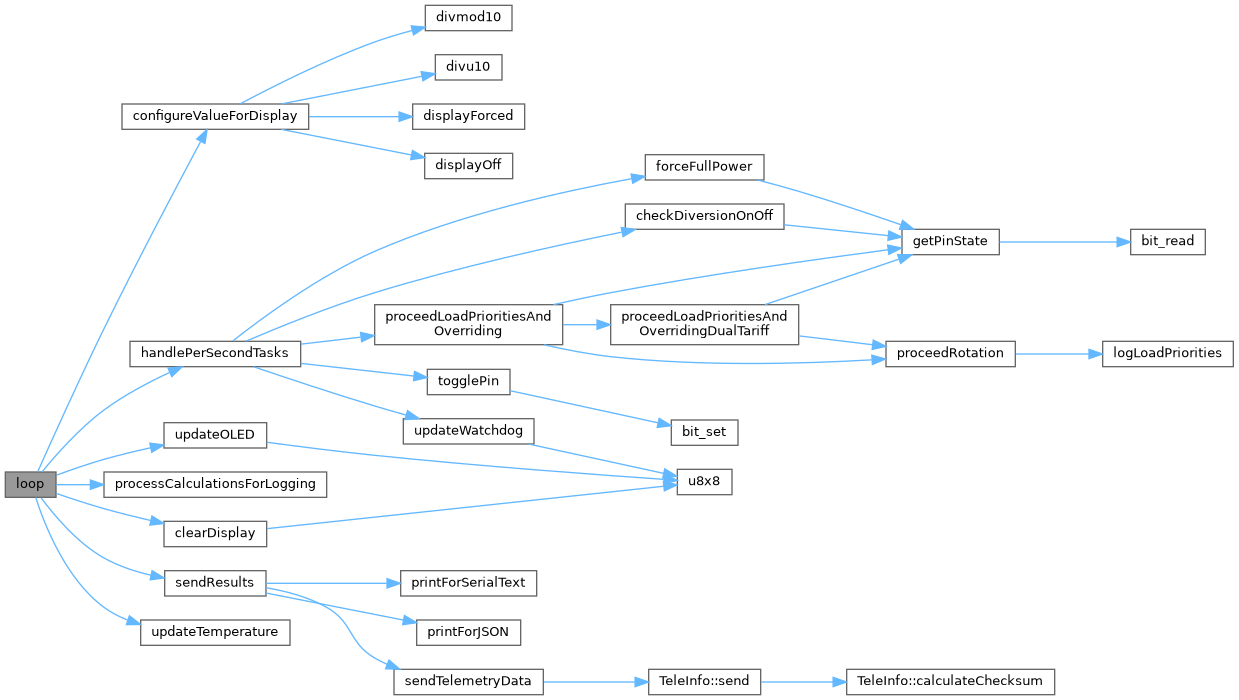
| void loop | ( | ) |
Main processor loop.
This function is the main execution loop of the program. It handles periodic tasks, including refreshing the display, managing load priorities, processing data for logging, and sending results. The loop is designed to handle non-time-critical tasks, as all time-sensitive operations are performed within the Interrupt Service Routine (ISR).
Key operations include:
- Incrementing timers for periodic tasks.
- Refreshing the display at a defined interval.
- Managing energy diversion and load priorities.
- Processing accumulated data for logging purposes.
- Sending results to external systems.
- Note
- The loop relies on several global variables and flags, such as
b_newCycle,b_datalogEventPending, andabsenceOfDivertedEnergyCount. It also uses compile-time constants likeSUPPLY_FREQUENCYandUPDATE_PERIOD_FOR_DISPLAYED_DATA.
Definition at line 487 of file main.cpp.
References Shared::b_datalogEventPending, Shared::b_diversionEnabled, Shared::b_newCycle, Shared::b_overrideLoadOn, clearDisplay(), configureValueForDisplay(), Shared::copyOf_divertedEnergyTotal_Wh, Shared::copyOf_divertedEnergyTotal_Wh_forDL, Shared::EDD_isActive, handlePerSecondTasks(), processCalculationsForLogging(), RELAY_DIVERSION, relays, sendResults(), SUPPLY_FREQUENCY, tx_data, UPDATE_PERIOD_FOR_DISPLAYED_DATA, updateOLED(), and updateTemperature().
◆ proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverriding()
| bool proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverriding | ( | const int16_t | currentTemperature_x100 | ) |
Handles load priority rotation and overriding logic.
This function manages the load priorities and overrides based on the current system state. Since the system does not have access to a clock, it detects the start of the off-peak period using the main energy meter. When the off-peak period starts, the function rotates the load priorities for the next day. It also supports dual tariff systems, rotation after a specified time, and manual overrides using a force pin. The function detects transitions between off-peak and peak periods and triggers load priority rotations accordingly.
Key operations include:
- Detecting off-peak and peak period transitions.
- Rotating load priorities automatically or based on user input.
- Managing load overrides using a force pin.
- Parameters
-
currentTemperature_x100 The current temperature multiplied by 100 (e.g., 25.00°C is represented as 2500). Used for temperature-based load override logic.
- Returns
- true if the off-peak tariff is active.
- false if the on-peak tariff is active.
- Note
- This function relies on several compile-time constants and global variables, such as
DUAL_TARIFF,EMONESP_CONTROL,PRIORITY_ROTATION, andOVERRIDE_PIN_PRESENT.
Definition at line 216 of file main.cpp.
References Shared::absenceOfDivertedEnergyCountInSeconds, AUTO, Shared::b_overrideLoadOn, DBUGLN, DUAL_TARIFF, EMONESP_CONTROL, forcePin, getPinState(), OVERRIDE_PIN_PRESENT, proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverridingDualTariff(), proceedRotation(), ROTATION_AFTER_SECONDS, and rotationPin.
Referenced by handlePerSecondTasks().


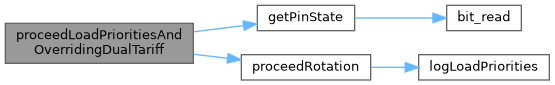
◆ proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverridingDualTariff()
| bool proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverridingDualTariff | ( | const int16_t | currentTemperature_x100 | ) |
Handles load priority in combination with dual tariff.
This function manages load priorities and overrides during dual tariff operation. It detects transitions between off-peak and peak periods using the state of the dual tariff pin. During the off-peak period, it rotates load priorities (if enabled) and manages load overrides based on the elapsed time and temperature thresholds. At the end of the off-peak period, it resets the state and logs the transition.
Key operations include:
- Detecting the start and end of off-peak periods.
- Rotating load priorities automatically during off-peak periods.
- Managing load overrides based on elapsed time and temperature thresholds.
- Parameters
-
currentTemperature_x100 The current temperature multiplied by 100 (e.g., 25.00°C is represented as 2500). Used for temperature-based load override logic.
- Returns
- true if the high tariff (on-peak period) is active.
- false if the low tariff (off-peak period) is active.
- Note
- This function relies on several compile-time constants and global variables, such as
PRIORITY_ROTATION,NO_OF_DUMPLOADS, andrg_OffsetForce.
- See also
- proceedRotation
- getPinState
Definition at line 142 of file main.cpp.
References AUTO, Shared::b_overrideLoadOn, DBUGLN, dualTariffPin, forcePin, getPinState(), i, iTemperatureThreshold, NO_OF_DUMPLOADS, proceedRotation(), rg_OffsetForce, and ul_TimeOffPeak.
Referenced by proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverriding().

◆ proceedRotation()
| void proceedRotation | ( | ) |
Rotates the load priorities.
This function triggers a reordering of load priorities. It sets a flag to indicate that the priorities need to be rotated and waits until the rotation is completed within the Interrupt Service Routine (ISR). Once the rotation is done, it logs the updated load priorities for debugging or monitoring purposes.
Key operations include:
- Setting the
b_reOrderLoadsflag to initiate priority rotation. - Waiting for the ISR to complete the rotation.
- Logging the updated load priorities.
- Note
- This function uses a delay to wait for the ISR to complete the rotation. Ensure that the delay duration is appropriate for the system's timing requirements.
- See also
- logLoadPriorities
Definition at line 102 of file main.cpp.
References Shared::b_reOrderLoads, and logLoadPriorities().
Referenced by proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverriding(), and proceedLoadPrioritiesAndOverridingDualTariff().

◆ processCalculationsForLogging()
| void processCalculationsForLogging | ( | ) |
Performs calculations on data for logging purposes.
This function processes accumulated data over a logging period to calculate key metrics such as power grid usage, diverted power, and voltage. These calculations are based on the number of sample sets collected during the logging period and calibration constants.
The function also adjusts the calculated voltage based on the logging period duration (e.g., for periods longer than 10 seconds, a scaling factor is applied).
- Note
- This function relies on global variables such as
Shared::Shared::copyOf_sumP_grid_overDL_Period,Shared::copyOf_sampleSetsDuringThisDatalogPeriod, andf_voltageCal.
- See also
- sendResults
- updateTemperature
Definition at line 350 of file main.cpp.
References Shared::copyOf_sampleSetsDuringThisDatalogPeriod, Shared::copyOf_sum_Vsquared, Shared::copyOf_sumP_diverted_overDL_Period, Shared::copyOf_sumP_grid_overDL_Period, DATALOG_PERIOD_IN_SECONDS, f_voltageCal, powerCal_diverted, powerCal_grid, and tx_data.
Referenced by loop().

◆ setup()
| void setup | ( | ) |
Called once during startup.
This function initializes various components and settings required for the program to run. It sets up the serial communication, initializes the display, configures optional pins, and ensures all loads are turned off at startup. Additionally, it logs the load priorities and initializes temperature sensors if present.
Key operations include:
- Delaying to allow time for the Serial monitor to open.
- Initializing the Serial interface and debug port.
- Setting up the OLED display and initializing it.
- Configuring optional pins and logging load priorities.
- Initializing temperature sensors if the feature is enabled.
- Printing the available free RAM for debugging purposes.
- Note
- This function is executed only once at the beginning of the program.
Definition at line 391 of file main.cpp.
References DBUG, DBUGLN, delayBeforeSerialStarts, freeRam(), initializeDisplay(), initializeProcessing(), IoT, logLoadPriorities(), printConfiguration(), SERIAL_OUTPUT_TYPE, setupOLED(), TEMP_SENSOR_PRESENT, and temperatureSensing.
◆ updateTemperature()
| void updateTemperature | ( | ) |
Updates the temperature readings and sends a new request for the next cycle.
This function reads the temperature values from the sensors, validates them, and updates the global temperature data. If a temperature reading is invalid (e.g., disconnected sensor or out-of-range value), it is replaced with a default value (DEVICE_DISCONNECTED_RAW). After processing the current readings, the function sends a new request to the sensors to prepare for the next cycle.
Key operations include:
- Reading temperature values from all sensors.
- Validating the temperature readings.
- Updating the global temperature data structure.
- Sending a new request to the sensors for the next cycle.
- Note
- This function is only executed if the
TEMP_SENSOR_PRESENTcompile-time constant is defined.
Definition at line 312 of file main.cpp.
References DEVICE_DISCONNECTED_RAW, TEMP_SENSOR_PRESENT, temperatureSensing, and tx_data.
Referenced by loop().
Generated by